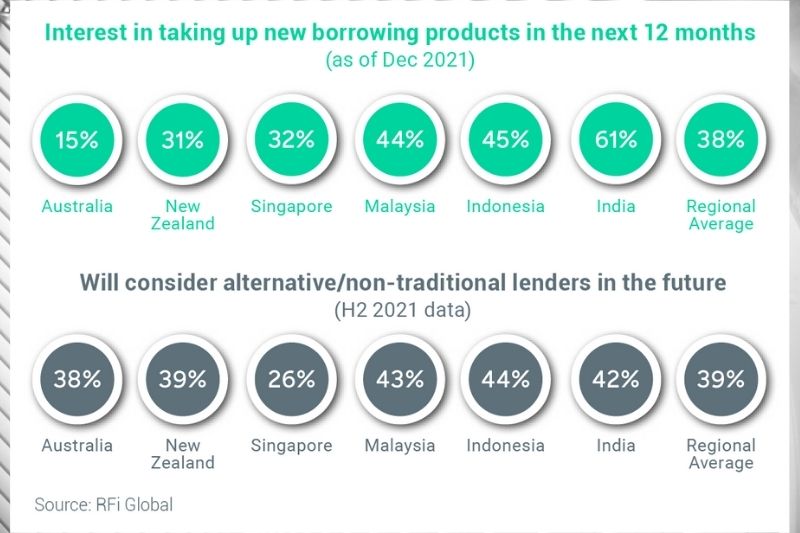
New insights from RFI Global (prepared for FICO based on research from the SME Banking Council) reveal early signs that traditional banks in Malaysia are at risk of losing small- and medium-sized enterprise (SME) business to non-traditional competitors.
Amidst strong interest in borrowing funds, between 62-70 percent of APAC SMEs are less than satisfied with their main bank’s level of support in response to the COVID-19 outbreak. Nearly 60 percent of Malaysia’s SMEs expect to take up new or alternative / non-traditional borrowing products in 2022.
More information: https://www.fico.com/en/latest-thinking/white-paper/what-do-smes-need-their-banking-providers-post-pandemic
“The pandemic put a sudden, massive burden on SMEs, globally, and they didn’t think banks did enough to help them,” said Aashish Sharma, senior director of decision management solutions in Asia Pacific for FICO. “Malaysia’s SMEs have made it clear that that they require financial support in 2022 but are less optimistic about getting it from their main banks. This is a potentially worrying trend for traditional banks, considering there are an estimated 1.15 million SMEs in Malaysia, employing about 48 percent of the workforce and contributing just over 38% percent of the GDP (Gross Domestic Product).”
Verdict: Room for Improvement
Banks need to understand what’s causing SMEs to consider alternative funding sources. Survey respondents across the Asia Pacific region pointed to frustrations with the typical funding process of traditional banks and identified room for improvement in their Covid-19 response across a range of funding related factors including:
- Access to credit (70 percent)
- Financial assistance (69 percent)
- Information and guidance (68 percent)
- Transparency re: decisions and processes (68 percent)
- Speed of response (64 percent)
SMEs call for competitive rates, simplified processes
According to this latest research, when choosing a loan provider or financial institution, the top three drivers for Malaysian SMEs are:
1. Competitive interest rates
2. Ease and speed of application process
3. Flexibility in repayment options
“Alternative lenders have the potential to gain ground based on the challenges identified by this research and by our own market observations,” said Sharma. “However, the opportunity is there for traditional banks to retain borrowers if they understand those key decisioning criteria alongside the challenges and funding support sentiments of SME and the themes that have emerged.”
“If traditional banks are to experience continued and sustainable business growth from the SME segment in the APAC region, they must simplify the application process and improve transparency, as well as customer experience,” continued Sharma. “From the banks’ risk management perspective, they can support these efforts with scalable, well-informed decisioning tools that can both speed up the process for all and minimize risk.”
The results speak for themselves
One of Australia’s top-four banks wanted to boost sales and margins by cutting down decision-making time, whilst improving lending services and identified the SME segment as an area for growth. It invested in FICO Platform and analytic services to create an automated, machine learning-powered digital lending solution that utilized transaction data. Risk model performance improved by 10 percent, and the bank’s projections for annual lending to existing SME customers and incremental lending to new SME customers increased by AUD $6.5 billion and AUD $800 million, respectively.